Hard drives come with integrated memory cache as part of their
design. The cache improves performance by providing the system with fast
access to frequently-used data. However, not all frequently-used data
can be contained because the cache’s size is usually limited to just a
few megabytes. Increasing the
amount of a hard drive’s cache, therefore, will make it perform better.
Aside from memory chips planted on the hard drive itself, this cache can
also be provided by another storage media.

The above principle is incorporated by Intel in its
recently-introduced Smart Response Technology, which enables hard drives
caching via solid state disk
(SSD), thus providing the hard drive with larger cache capacity (by
using the SSD as additional cache). This improves computer performance,
but both the hard drive and SSD must be joined together in RAID
configuration. With the Synapse, OCZ took a rather different approach by
dedicating this SSD for the sole purpose of hard drive caching.

OCZ Synaps comes with the company’s DataPlex software, whose function
is none other than turning the Synapse to a “cache drive”. While its
intended purpose is to serve as a “cache extension” of your main hard
drive, there are still quite a few possibilities one could expect from
the Synaps. Imagine, for example, pairing the Synapse with a low-energy
consumption 2 TB hard drive (whose performance is usually the lowest
among hard drives) to get a large storage media that performs almost as
good as a “real” SSD. Of course, a 2 TB SSD would be massively
expensive, if available at all. This is where OCZ Synaps comes in: it
seeks to combine SSD’s super fast performance with the large capacity of
a conventional hard drive without breaking your bank.
This is the first article in a set of two that will explore the
capabilities of OCZ Synapse. For now, we’re going to explore the SSD’s
performance as a standalone drive. Before we begin, let’s take a look at
the hardware components that we use as testbed.
Test Platform
- Motherboard: Intel H67 LGA 1155
- Prosesor: Intel Core i7 2600 3,4 GHz
- RAM: Kingston DDR3 8 GB
- Storage: Kingston SSD V+100 64 GB
- Graphics Card: AMD Radeon HD 5550
- Power Supply: CoolerMaster GX 550 Watt
- Input Device: Genius Keyboard and Mouse
- Monitor: 18,5 inch LCD
- Sistem Operasi: Microsoft Windows 7 64 bit
Sales Package and Contents
This is how the package box looks like.

Inside it, you will find the following items:



Test Results
HDTune
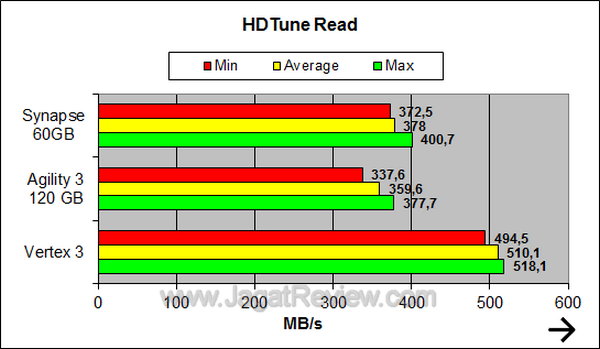
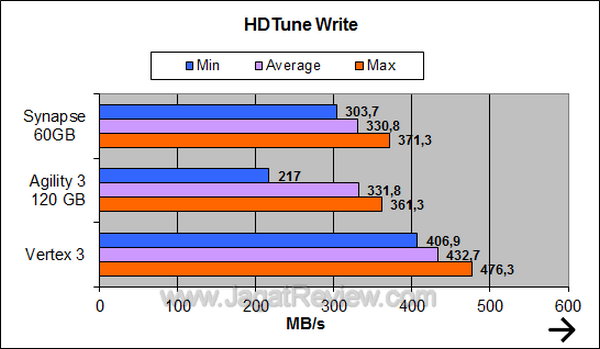

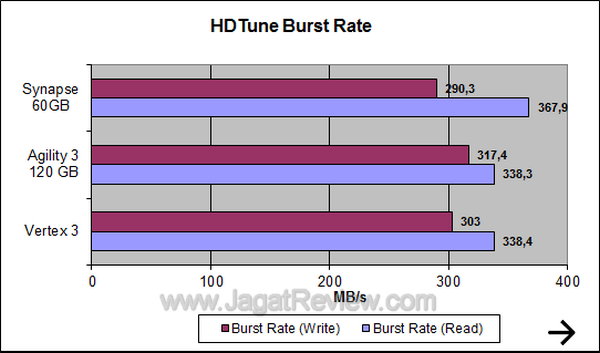
HDTune shows that the Synapse has a higher read performance than Agility 3.
I/O Meter
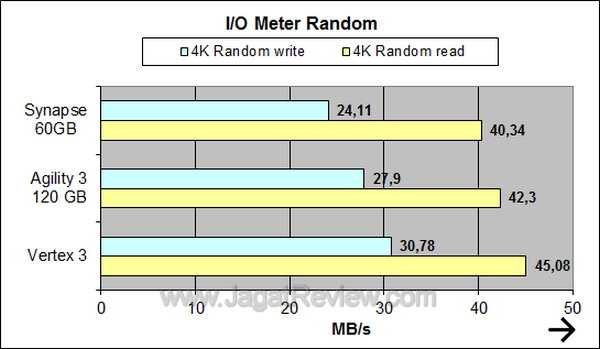

Synapse performs similarly with Agility 120 GB here in I/O meter.
Crystal Disk Mark
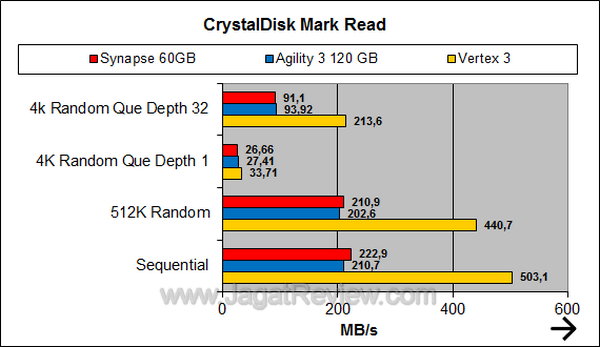
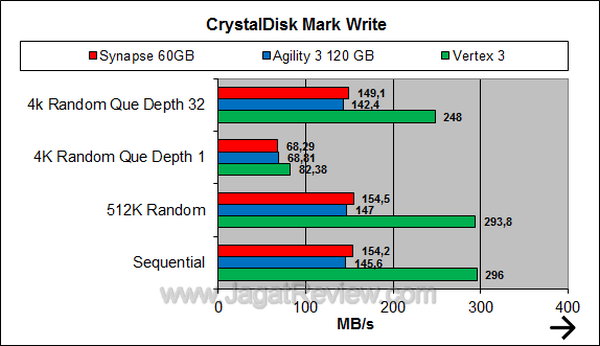
Like in the two previous benchmarks, Crystal Disk Mark confirms Synapse’s remarkable performance. As a standalone SSD, its performance is comparable to that of the Agility 3.
PCMark 7
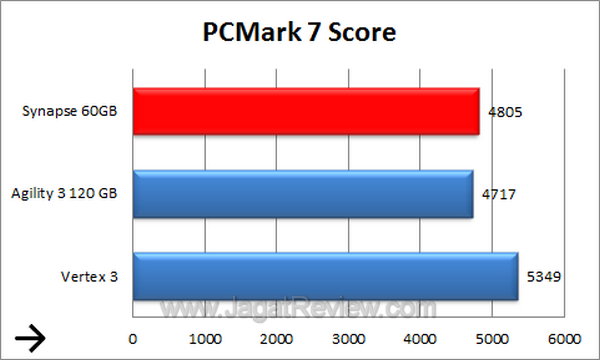
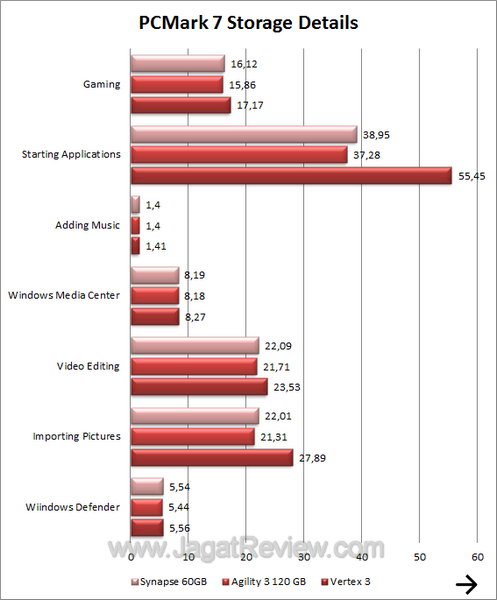
In PC Mark, Synapse even performs a bit better than Agility 3.
Transfer Test
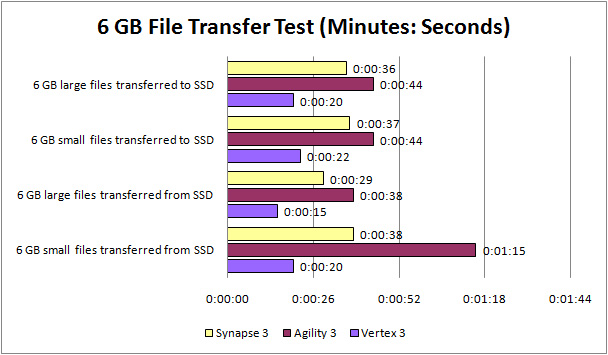
Last but not least, we have the real world test, where Synaps once again performs better than the 120 GB version of Agility 3.
Conclusions
For a 60 GB SSD meant for hard drive caching purposes, OCZ Synaps shows remarkable performance on its own. At times, it could even transfer data faster than Agility 3 120 GB. The Vertex 3 is in an entirely different league though, so you shouldn’t expect Synapse to compete directly against it. Unfortunately, Synapse comes with a rather hefty price tag of around US$ 150, perhaps due to its intended use as hard drive “accelerator”, instead of main boot drive.From the benchmarks, Synapse looks promising. Could it actually speed up your hard drive? If so, then how much performance increase can you expect? Find the answer in our second article!
Pros:
+ High performance
+ DataPlex Software bundle
+ Durable
+ TRIM capability
Cons:
- Rather expensive for a 60 GB SSD
Technical Data
| Manufacturer | OCZ |
| Info | http://www.ocztechnology.com/ |
| Price | - |
| Distributor in Indonesia | Spectrum |
| Phone | 021 612 5505 |
| Memory Type | Multi Level Cell |
| Capacity | 60 GB |
| Interface | SATA 6 Gbps |








0 comments:
Post a Comment